GVST GClip
Wave-shaping signal clipper - free VST audio effect plug-in download for music production, broadcasting and general audio editing.
- Clip peaks off audio with abrupt or smooth wave-shaping.
- Graph and waveform displays assist in setting the clip level according to the source material.
- Oversampling can be enabled to reduce aliasing.
For more details, read through the online manual below.
GClip Manual
Welcome to GClip
GClip is a wave-shaping signal clipper.
It prevents the signal level from exceeding a specified maximum.
The clipping function used can be altered to have a hard- or soft-knee.
Interface
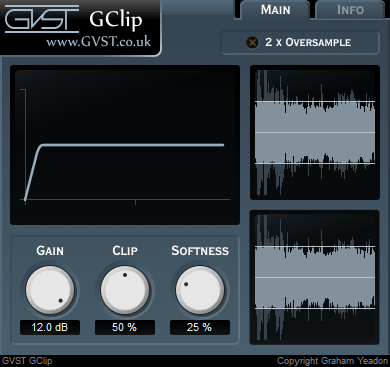
The display features three main areas.
At the top-left is the graph display, to the right is the wave display and at the bottom-left are the parameter controls.
Graph Display: This shows the shape of the clipping function that is applied to incoming samples.
All three knobs affect the shape of this curve.
Wave Display: This shows the waveform of the signal after the input gain has been applied.
Superimposed over that is the output signal, after clipping.
So you get a before and after display.
The clipping level is also displayed as a solid horizontal line.
Gain: This allows you to raise the signal level before clipping.
Clip: The clipping level as a percentage of the maximum sample value.
So, if you consider samples to go from -1 to 1, then a clipping level of 50% will restrict all samples to between -0.5 and 0.5.
Softness: This parameter sets the shape of the "knee" of the clipping function.
If this parameter is 0% then GClip behaves as a simple signal clipper, truncating samples that exceed the clipping level.
Greater values for softness will cause samples approaching the clipping level to be affected.
2x Oversample: Turn oversampling on or off.
Wave-shaping can introduce audible aliasing, especially with more drastic settings.
The oversampling mode can help to minimize aliasing in such cases.
Hints and ideas
-
The user interface features a wave display to aid configuration.
Simply play the audio and watch the wave display while you set the desired values for input gain, clip-level and softness.
And don't forget to use your ears as well.
-
You can create a distortion effect with excessive gain and harsh clipping.
On the other hand, if you're not after distortion, then listen carefully to sections that are reaching the clip threshold.
-
When using GClip for more extreme wave-shaping, the oversampling mode can reduce aliasing for a warmer sound.

