GVST GSinthG
Pitch-tracking synth effect - free VST audio effect plug-in download for music production, broadcasting and general audio editing.
- Tracks the pitch of a monophonic input signal.
- Uses the detected pitch to drive a monophonic synth.
- Design for use as a guitar-driven synth, but only for melodic lines without double-stops or chords.
For more details, read through the online manual below.
GSinthG Manual
Welcome to GSinthG
GSinthG is a pitch-driven synthesizer, allowing the synth to be played with a monophonic input signal, e.g. a (carefully played) guitar or a voice.
Interface
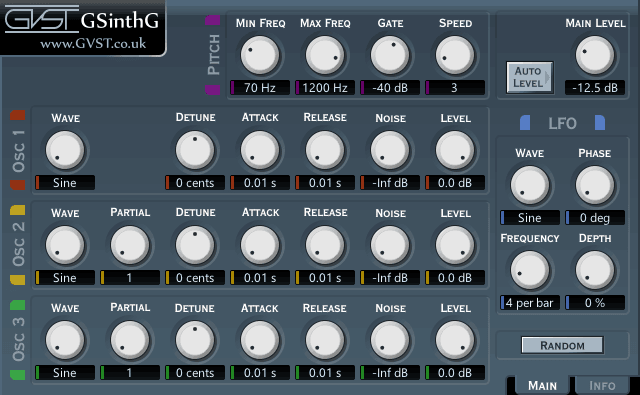
The user interface has a lot of controls, but many are duplicated across the three oscillators in the synthesizer.
There are a few broad areas, which we'll deal with in turn here.
Pitch
These controls relate to the pitch-tracking that drives the synthesizer.
Min Freq, Max Freq: These define the lower and upper frequencies that the pitch tracker will look for.
Setting these to ignore frequencies below or above those expected for the source intstrument can help improve the accuracy and efficiency of pitch-detection.
Gate: This is similar to the frequency limiting parameters. It this specifies a lower limit for signal level.
The pitch detection will ignore the input if it drops below this level. Again, this helps to make the pitch detection more efficient and accurate.
Speed: The Speed parameter sets the number of wave repetitions required for pitch-detection.
Lower values for Speed will allow faster pitch-detection but increase the chance of false detection.
Higher values will mean pitch-detection is more confident, but slower.
The default value should be fine in most cases.
Oscillators
Wave: Select the waveform for each oscillator: sine, triangle, square or sawtooth.
Partial: The frequency of oscillator 2 and 3 can be set as a multiple of the fundamental frequency, allowing a small degree of additive synthesis.
Detune: Allow each oscillator to be detuned by +/- 99 cents.
A little detuning can help thicken the synth sound, a lot can just sound dissonant.
Attack, Release: These define a simple attack and release envelope for the synthesised notes.
Unlike a MIDI synth, there is no keyboard triggering a note, instead notes are triggered by the pitch tracking.
When a pitch is detected, that triggers a note with the specified attack.
When the incoming note ends, the synthesised note will be released.
Noise: Just adds some white noise to the oscillator to create a "dusty" character.
Level: Controls the level of each oscillator.
Main Level
Main Level: Controls the overall output level.
Auto level: Clicking this button makes GSinthG look at the other settings and then select an optimised overall level that prevents clipping.
LFO
The LFO is synchronised to the host clock and varies the main output level according to the settings.
(Not all hosts will support synchronising to the host tempo).
Wave: Select the waveform for the LFO: sine, triangle, square, rising, falling or random.
Frequency: Set the frequency in terms of cycles per bar, according to the host tempo (if supported).
Phase: Adjust the phase of the waveform at the start of each bar.
Depth: Set the depth of the LFO level variation.
Hints and ideas
-
GSinthG can be applied to a recorded track, but it can also be fun to play live.
-
The effect could be used to create a synth part that mirrors a recorded guitar or vocal melody.

